Harmful Effects of Climate Change in Bangladesh

Joynal Abedin।। Global climate change is also having temporary or permanent negative effects on Bangladesh. This environmental disaster due to climate change has been identified as a long-term problem in the National Environment Management Action Plan prepared by the Bangladesh Ministry of Forest and Environment, Government of Bangladesh. Whether a country is really affected by climate change or not is considered based on four criteria: 1. Who is most affected by climate change 2. Where are natural disasters more common 3. Where is the largest population affected and 4. What steps have the affected country already taken to cope with the damage or adapt?
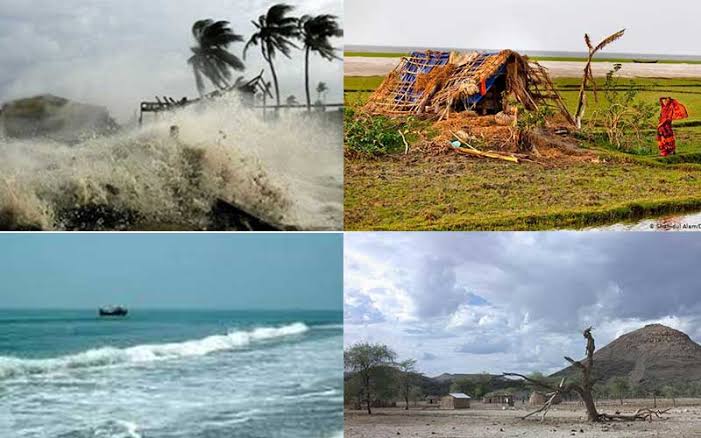
Bangladesh is being affected by sea level rise, salinity problems, changes in river direction due to melting of Himalayan glaciers, floods, etc. in all aspects. Apart from this, the level of natural disasters is also very high. Therefore, Bangladesh is at the top of the list of those affected by climate change in all four criteria mentioned above. According to the Global Climate Risk Index published by the international research organization German Watch in 2010, Bangladesh is ranked first among the top 10 countries affected by damage due to climate change. This survey was conducted on 193 countries from 1990 to 2009. It is worth noting that Bangladesh was the most affected country in the reports published by the organization in 2007 and 2008.
The country has had seasonal variations since ancient times. Due to its six seasons, the country is also called the country of six seasons. The monsoon season lasts from June to October. During this time, there is a lot of rainfall here due to the influence of monsoon winds, which often leads to flooding. In addition, at the beginning or immediately after the departure of monsoon winds, natural disasters such as cyclones, tornadoes on land or low pressure in the sea, cyclones, tidal waves, etc. occur, which almost regularly affect Bangladesh. But this natural picture of Bangladesh has now changed a lot due to the direct impact of climate change. These changes in temperature, rainfall, wind flow, and sea level have caused drastic climatic changes in Bangladesh.
Due to the decrease in rainfall due to climate change, the water flow of rivers is not at its normal level during the dry season. As a result, due to the huge pressure of river water, the salty water of the sea is not trapped in the area as much as it should be. Due to the low water flow, the salty water of the sea comes closer to the land. As a result, salinity increases in large areas of the coastal region of the country. Experts are of the opinion that the problem of salinity in coastal areas will become more pronounced day by day due to low rainfall. Due to the increase in salinity due to the rise in sea level, the sundari trees of the Sundarbans have already seen widespread agamra disease. Although many want to attribute it to man-made causes, researchers have identified it as a natural cause. Other trees in the Sundarbans are also being attacked by agamra and leaf skeletonizing insects. The vine garden is also being affected.
Although Bangladesh is known as a country with temperate temperatures, that reputation has been fading in the past few years due to the unusual behavior of temperatures. In 1960, the highest temperature recorded in Bengal was 42.3 degrees Celsius. After independence, on May 30, 1972, the temperature in Bangladesh was recorded at 45.1 degrees Celsius in Rajshahi. In 1995, it was recorded at 43 degrees Celsius. On April 26, 2009, the highest temperature in the last 14 years was recorded at 42.2 degrees Celsius in Jessore.
Although these temperature statistics seem to indicate that the temperature is decreasing, in fact, the maximum average temperature in the past was low, while the current maximum average temperature is extremely high. Because, according to a study by the World Wildlife Fund, the average temperature in Dhaka city alone in May has increased by 1 degree Celsius compared to that month in 1995? In November, this temperature has increased by 0.5 degree Celsius compared to 14 years ago? According to the Meteorological Department, the country’s temperature has increased by 0.5 percent in the last 50 years. It is even estimated that the temperature in Bangladesh will increase by an average of 1.4 degrees Celsius by 2050 and 2.4 degrees Celsius by 2100.
Rainfall is decreasing day by day, floods are not happening on time. In 2008, the average rainfall in Bangladesh was 2300 millimeters, while the average rainfall in the Barendra area was 1150 millimeters. Such low rainfall is increasing day by day. As a result, the groundwater level will drop and a large number of people will be affected by drought, most of whom are people in the northern part of Bangladesh. Different data is available from different sources regarding how many people will be affected by such drought. According to some, about 8 million people will be displaced by drought by 2050 due to climate change. The groundwater level is decreasing in various places, resulting in permanent desertification. The water level is decreasing in the Barendra area of Rajshahi due to the decrease in rainfall. Although man-made factors, especially the effect of the Farakka Barrage in India, are also responsible for this. However, the decrease in groundwater level due to drought is particularly significant. Apart from this, the widespread use of groundwater due to the lack of potable water is also decreasing the groundwater.
The report prepared by the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change on the impact of climate change on water resources says that several coastal countries, including Bangladesh, will face a severe shortage of fresh water in the coming days. Due to the impact of climate change, various natural disasters have increased in Bangladesh. Among them, the increase in the level of cyclones, tidal waves, floods, river erosion and landslides is notable. While there used to be a major natural disaster every 15 or 20 years, now major disasters are striking every two to three years? Even in the list of the British research company Maplecraft, Bangladesh is ranked first among the 15 countries at risk due to natural disasters.
Due to the impact of climate change, various natural resources are gradually decreasing in Bangladesh. Many species are disappearing. This is affecting everything from trees, fish, birds, flowers, and fruits.
According to UNESCO’s report titled ‘Climate Change and World Heritage Lessons’, 75 percent of the Sundarbans could be destroyed due to various reasons including global climate change, including sea level rise? It is undeniable that the reduction of this huge amount of natural resources will have a huge adverse impact on the environment. Climate change is also having a major impact on the fisheries sector. Abnormal rainfall patterns and rising temperatures are constantly creating unfavorable conditions for the country’s fisheries. Due to lack of seasonal rainfall and untimely heavy rainfall, various problems are occurring in fish reproduction, such as the lack of suitable breeding environments and the high temperatures, which hinders reproduction. Due to this, eggs are being absorbed into the body.
A large number of animals in the country will be lost or significantly reduced due to the rise in sea level. If the height of the sea’s saltwater increases, the forest area suitable for the Royal Bengal Tiger in Khulna’s Sundarbans will decrease. This will reduce the prey of tigers. As a result, the number of tigers will naturally decrease significantly. The dolphins roaming the Ganges will decrease. The Maya deer will disappear forever. The Chitra deer will also decrease. The conch snake will decrease. The masked kinfoot will become completely extinct. Experts believe that the Palash fish eagle may also become extinct. However, the number of pests, such as mosquitoes, will increase. The increase in the number of pests will take a serious form.
In agriculture-dominated Bangladesh, where there was a suitable temperature and six distinct seasons for agricultural production, seasons are disappearing day by day due to climate change, and with it, there are radical changes in rainfall and temperature. As a result, the future of agriculture in Bangladesh is facing extreme threats due to various problems such as irregular, insufficient rainfall, insufficiency of irrigation water, coastal flooding at different times in addition to the monsoon season in coastal areas, land being submerged in saline water due to rising sea levels, and saline water flowing upwards or sideways in the dry season. Due to the impact of climate change, subsistence farmers dependent on the natural environment will lose their livelihoods and become unemployed. This will exacerbate the unemployment problem in the country. For example, if fish production decreases, freshwater fishermen, sea-going fishermen, coastal fishermen and their families will lose their source of livelihood.
The people of Bangladesh are facing various health risks due to the adverse effects of climate change. Respiratory problems, heatstroke or heat-related deaths, or severe cold-related deaths, etc. have now become very common. The social system of Bangladesh will be affected by the effects of global climate change. A large number of people are being affected by the increasing rate of natural disasters in coastal areas. These homeless refugees are taking shelter in nearby big cities or in the capital city. As a result, the population of those cities is increasing. Those cities are struggling to cope with the pressure of the additional population. As additional sources of income are not created for the additional population, the displaced people choose the path of various crimes. Chaos begins to appear in society, and law and order deteriorates day after day. Bangladesh has to allocate a huge amount of money in the budget every year to deal with climate change at the national level. As a result, other necessary development activities of the government are being hampered.